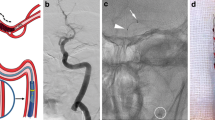
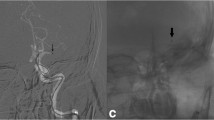
Abstract
Background and Purpose
Direct thrombus aspiration is increasingly used as a first-line therapy in acute ischemic stroke with large vessel occlusion. We assessed the performance and safety of a novel aspiration catheter available: the 6-French AXS Catalyst catheter.
Materials and Methods
We conducted a cohort study from a prospective clinical registry of consecutive stroke patients treated by mechanical thrombectomy between March 2016 and July 2016. Baseline clinical and imaging characteristics, recanalization rates, complications, and clinical outcomes were analyzed.
Results
Among the 60 patients included, 30 were treated using aspiration alone, 14 were treated using aspiration and then stent retriever as a rescue therapy, and 16 were treated using aspiration combined with a stent retriever straightaway. Successful recanalization (mTICI2b/3) was achieved in 85% patients and functional independence in 48.3%. We observed one intracranial perforation and one vertebral artery dissection. Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage occurred in 5% and mortality in 21.7%.
Conclusion
Endovascular stroke therapy using the AXS Catalyst catheter seems safe and effective, with similar performance than other reperfusion catheters.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AIS:
-
Acute ischemic stroke
- ADAPT:
-
A Direct Aspiration First Pass Technique
- HI:
-
Hemorrhagic infarction
- ICA:
-
Internal carotid artery
- IVT:
-
Intravenous thrombolysis
- LVO:
-
Large vessel occlusion
- MCA:
-
Middle cerebral artery
- MT:
-
Mechanical thrombectomy
- mTICI:
-
Modified Thrombolysis In Cerebral Infarction
- PH:
-
Parenchymal hemorrhage
- sICH:
-
Symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage
References
Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0000000000000158.
Lapergue B, Blanc R, Gory B, Labreuche J, Duhamel A, Marnat G, et al. Effect of endovascular contact aspiration vs stent retriever on revascularization in patients with acute ischemic stroke and large vessel occlusion: the ASTER randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318:443–52.
Turk AS, Frei D, Fiorella D, Mocco J, Baxter B, Siddiqui A, et al. ADAPT FAST study: a direct aspiration first pass technique for acute stroke thrombectomy. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014;6:260–4.
Massari F, Henninger N, Lozano JD, Patel A, Kuhn AL, Howk M, et al. ARTS (aspiration-retriever technique for stroke): initial clinical experience. Interv Neuroradiol. 2016;22:325–32.
Maus V, Behme D, Kabbasch C, Borggrefe J, Tsogkas I, Nikoubashman O, et al. Maximizing first-pass complete reperfusion with SAVE. Clin Neuroradiol. 2017;28:1–12.
Ferrigno M, Bricout N, Leys D, Estrade L, Cordonnier C, Personnic T, et al. Intravenous recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator: influence on outcome in anterior circulation ischemic stroke treated by mechanical thrombectomy. Stroke. 2018;49:1377–85.
Adams HP, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, et al. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in acute stroke treatment. Stroke. 1993;24:35–41.
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C, von Kummer R, Davalos A, Meier D, et al. Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial of thrombolytic therapy with intravenous alteplase in acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS II). Second European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study Investigators. Lancet Lond Engl. 1998;352:1245–51.
van Swieten JC, Koudstaal PJ, Visser MC, Schouten HJ, van Gijn J. Interobserver agreement for the assessment of handicap in stroke patients. Stroke. 1988;19:604–7.
Neeb L, Villringer K, Galinovic I, Grosse-Dresselhaus F, Ganeshan R, Gierhake D, et al. Adapting the computed tomography criteria of hemorrhagic transformation to stroke magnetic resonance imaging. Cerebrovasc Dis Extra. 2013;3:103–10.
Zaidat OO, Yoo AJ, Khatri P, Tomsick TA, von Kummer R, Saver JL, et al. Recommendations on angiographic revascularization grading standards for acute ischemic stroke: a consensus statement. Stroke. 2013;44:2650–63.
Togay-Işikay C, Kim J, Betterman K, Andrews C, Meads D, Tesh P, et al. Carotid artery tortuosity, kinking, coiling: stroke risk factor, marker, or curiosity? Acta Neurol Belg. 2005;105:68–72.
Goyal M, Menon BK, Van Zwam WH, Dippel DW, Mitchell PJ, Demchuk AM, et al. Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet. 2016;387:1723–31.
Quinn TJ, Taylor-Rowan M, Coyte A, Clark AB, Musgrave SD, Metcalf AK, et al. Pre-stroke modified rankin scale: evaluation of validity, prognostic accuracy, and association with treatment. Front Neurol. 2017;8:275.
Dobrocky T, Piechowiak E, Cianfoni A, Zibold F, Roccatagliata L, Mosimann P, et al. Thrombectomy of calcified emboli in stroke. Does histology of thrombi influence the effectiveness of thrombectomy? J NeuroInterv Surg. 2018;10:345–50.
Gunning GM, McArdle K, Mirza M, Duffy S, Gilvarry M, Brouwer PA. Clot friction variation with fibrin content; implications for resistance to thrombectomy. J Neurointerv Surg. 2017;10:34–8.
Kidwell CS, Chalela JA, Saver JL, Starkman S, Hill MD, Demchuk AM, et al. Comparison of MRI and CT for detection of acute intracerebral hemorrhage. JAMA. 2004;292:1823–30.
Goyal M, Menon BK, van Zwam WH, Dippel DWJ, Mitchell PJ, Demchuk AM, et al. Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet. 2016;387:1723–31.
Vora NA, Gupta R, Thomas AJ, Horowitz MB, Tayal AH, Hammer MD, et al. Factors predicting hemorrhagic complications after multimodal reperfusion therapy for acute ischemic stroke. Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28:1391–4.
Mocco J, Zaidat OO, von Kummer R, Yoo AJ, Gupta R, Lopes D, et al. Aspiration thrombectomy after intravenous alteplase versus intravenous alteplase alone. Stroke. 2016;47:2331–8.
Blanc R, Redjem H, Ciccio G, Smajda S, Desilles J-P, Orng E, et al. Predictors of the aspiration component success of a direct aspiration first pass technique (ADAPT) for the endovascular treatment of stroke reperfusion strategy in anterior circulation acute stroke. Stroke. 2017;48:1588–93.
Sallustio F, Pampana E, Davoli A, Merolla S, Koch G, Alemseged F, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy of acute ischemic stroke with a new intermediate aspiration catheter: preliminary results. J NeuroInterv Surg. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2017-013679.
Funding
This work was supported by Stryker Neurovascular. The funding source was not involved in study design, monitoring, data collection, statistical analyses, interpretation of results, or manuscript writing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for Publication
Consent for publication was obtained for every individual person’s data included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bretzner, M., Estrade, L., Ferrigno, M. et al. Endovascular Stroke Therapy with a Novel 6-French Aspiration Catheter. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 42, 110–115 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-018-2093-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-018-2093-y