Abstract
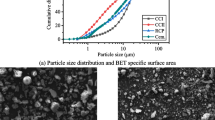
The present study aims at experimentally investigating the applicability of Ternary Blended Concrete (TBC) with Perlite Powder (PP) and Silica Fume (SF) as a partial replacement material which would offer resistance to elevated temperatures. In this direction, keeping the content of SF constant at 10%, four different TBC mixes were prepared by varying the content of PP from 1 to 7% with an increment of 2%, in addition to control concrete. The specimens, after being properly cured, were subjected to elevated temperatures in the range of 200–800 °C in steps of 200 °C, followed by air-drying. Experimental procedures like compression test, TGA-DTA, and XRD analysis were carried out. The results of these analyses show that TBC mix with 5% replacement of PP at 400 °C exhibited the highest strength and better thermal properties. An increased residual strength of about 30% was observed at 800 °C. Thermal analysis shows weight losses of 9.677%, 7.530%, and 1.596%, respectively, in the three phases of 5% PP is more, which is due to the presence of high pores. It is recommended that TBC with 5% PP and 10% SF be used as a good composite material with resistance to high temperatures.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulkareem, O. A., Al Bakri, A. M., Kamarudin, H., Nizar, I. K., & Ala’eddin, A. S. (2014). Effects of elevated temperatures on the thermal behavior and mechanical performance of fly ash geopolymer paste, mortar and lightweight concrete. Construction and Building Materials,50, 377–387.
Aldred, J. M., Holland, T. C., et al. (2006). Guide for the use of silica fume in concrete (p. 234). Farmington Hills: ACI—American Concrete Institute—Committee.
Brown, M. E. (1988). Differential thermal analysis (DTA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Introduction to thermal analysis (pp. 23–49). Dordrecht: Springer.
Celik, A. G., Kilic, A. M., & Cakal, G. O. (2013). Expanded perlite aggregate characterization for use as a lightweight construction raw material. Physicochemical Problems of Mineral Processing,49(2), 689–700.
Chandra, S., & Berntsson, L. (2002). Lightweight aggregate concrete. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Cui, S., Liu, P., Su, J., Cui, E., Guo, C., & Zhu, B. (2018). Experimental study on mechanical and microstructural properties of cement-based paste for shotcrete use in high-temperature geothermal environment. Construction and Building Materials,174, 603–612.
Demirboğa, R., & Gül, R. (2003). The effects of expanded perlite aggregate, silica fume and fly ash on the thermal conductivity of lightweight concrete. Cement and Concrete Research,33(5), 723–727.
Dubé, W. P., Sparks, L. L., & Slifka, A. J. (1992). Thermal conductivity of evacuated perlite at low temperatures as a function of load and load history. Construction and Building Materials,6(1), 19–22.
Erdem, T. K., Meral, C., Tokyay, M., & Erdoğan, T. Y. (2007). Use of perlite as a pozzolanic addition in producing blended cements. Cement & Concrete Composites,29(1), 13–21.
Fu, X., & Chung, D. D. L. (1997). Effects of silica fume, latex, methylcellulose, and carbon fibers on the thermal conductivity and specific heat of cement paste. Cement and Concrete Research,27(12), 1799–1804.
Ilić, B., Mitrović, A., Miličić, L., & Zdujić, M. (2018). Compressive strength and microstructure of ordinary cured and autoclaved cement-based composites with mechanically activated kaolins. Construction and Building Materials,178, 92–101.
Reddy, A. N., & Meena, T. (2018). A study on compressive behavior of ternary blended concrete incorporating alccofine. Materials Today: Proceedings,5(5), 11356–11363.
Sarkar, S. L., Satish, C., & Leif, B. (1992). Interdependence of microstructure and strength of structural lightweight aggregate concrete. Cement & Concrete Composites,14(4), 239–248.
Sengul, O., Azizi, S., Karaosmanoglu, F., & Tasdemir, M. A. (2011). Effect of expanded perlite on the mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of lightweight concrete. Energy and Buildings,43(2–3), 671–676.
Tasdemir, M. A., Tasdemir, C., Akyüz, S., Jefferson, A. D., Lydon, F. D., & Barr, B. I. G. (1998). Evaluation of strains at peak stresses in concrete: a three-phase composite model approach. Cement & Concrete Composites,20(4), 301–318.
Teja, K. V., & Meena, T. (2018). Study on temperature resistance concrete. International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology,9(4), 1229–1236.
Topçu, İ. B., & Işıkdağ, B. (2008). Effect of expanded perlite aggregate on the properties of lightweight concrete. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,204(1–3), 34–38.
Torres, M. L., & García-Ruiz, P. A. (2009). Lightweight pozzolanic materials used in mortars: Evaluation of their influence on density, mechanical strength and water absorption. Cement & Concrete Composites,31(2), 114–119.
Xu, L., Liu, S., Li, N., Peng, Y., Wu, K., & Wang, P. (2018). Retardation effect of elevated temperature on the setting of calcium sulfoaluminate cement clinker. Construction and Building Materials,178, 112–119.
Yu, L. H., Ou, H., & Lee, L. L. (2003). Investigation on pozzolanic effect of perlite powder in concrete. Cement and Concrete Research,33(1), 73–76.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank VIT University for providing ‘VIT SEED GRANT’ for carrying out this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teja, K.V., Meena, T. An insight into temperature characteristics of ternary blended concrete with perlite powder. Asian J Civ Eng 21, 41–48 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-019-00179-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-019-00179-1