Abstract
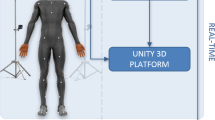
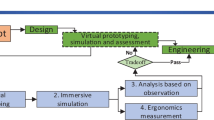
With the rapid development of information technology, the role of humans in complex human-machine systems has changed from manual workers to mental decision-makers. The human-machine interface’s spatial layout affects the operator's task flow and has a decisive effect on task performance. In order to meet the task requirements of the complex human-machine supervisory system, the human-machine interface layout should be evaluated for human-machine adaptability. In this paper, by means of 3D reproduction in virtual reality using motion capture, we mapped the operator's action joint data in real scene to the virtual scene to perform the final human-in-the-loop ergonomic assessment. Based on the spatial coordinate conversion algorithm, the joint attitude data was visualized in the virtual scene. Finally, through the RULA (Rapid Upper Limb Assessment) we completed the ergonomic assessment of human-machine interface layout. At the end we demonstrated an experiment which showed that the proposed method was valid and efficient.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Skřehot, P., Marek, J., Houser, F.: Ergonomic aspects in control rooms. Theor. Issues Ergon. Sci. 18(1), 46–58 (2017)
Wickens, C.D., Mccarley, J.S., Alexander, A.L., et al.: Attention-situation awareness (A-SA) model of pilot error. Human Perform. Model. Aviat. 213–239 (2008)
Parasuraman, R., Sheridan, T.B., Wickens, C.D.: A model for types and levels of human interaction with automation. IEEE Press. (2000)
Luke, T., Brook-Carter, N., Parkes, A.M., et al.: An investigation of train driver visual strategies. Cogn. Technol. Work 8(1), 15–29 (2006)
Kumar, G.S., Das, A.: Analysis and ergonomic improvement of working postures in cast house work station using JACK modelling. Int. J. Hum. Factors Modell. Simul. 3(1), 16–31 (2012)
Michoud, B., et al.: Real-time marker-free motion capture from multiple cameras. In: IEEE, International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2007, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil, October DBLP1–7 (2017)
Calderita, L.V., et al.: Model-based reinforcement of Kinect depth data for human motion capture applications. Sensors 13(7), 8835 (2013)
Puthenveetil, S.C., et al.: Computer-automated ergonomic analysis based on motion capture and assembly simulation. Virtual Real. 19(2), 119–128 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10055-015-0261-9
Jun, S.-K., et al.: Robotic minimally invasive surgical skill assessment based on automated video-analysis motion studies. In: 2012 4th IEEE RAS & EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronic (BioRob). IEEE (2012)
Biosyn Company, F.A.B system, Measurement Range, Accuracy, and Data Rate Specifications. http://biosynsystems.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/06/Sensor-Range-Accuracy.pdf
Mcatamney, L, Nigel, C.E.: RULA: a survey method for the investigation of work-related upper limb disorders. Appl. Ergon. 24(2), 91–99 (1993)
UIC 612. Driver machine interfaces for EMU/DMU, locomotives and driving coaches—functional and system requirements associated with harmonized Driver Machine Interfaces (2009)
Acknowledgments
The present work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities 2020RC013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bao, H., Guo, B., Ni, Q., Wang, J. (2021). Real-Time Ergonomic Assessment of Human-Machine Interface Layout Using Virtual Reality Reproduction. In: Rebelo, F. (eds) Advances in Ergonomics in Design. AHFE 2021. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 261. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-79760-7_76
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-79760-7_76
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-79759-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-79760-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)