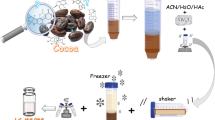
Abstract
Identifying the risk of ochratoxin A in our daily food has become fundamental because of its toxicity. In this work, we report a novel semi-automated in-syringe-based fast mycotoxin extraction (IS-FaMEx) technique coupled with direct-injection electrospray-ionization tandem mass spectrometer (ESI-MS/MS) detection for the quantification of ochratoxin A in coffee and tea samples. Under the optimized conditions, the results reveal that the developed method’s linearity was more remarkable, with a correlation coefficient of > 0.999 and > 92% extraction recovery with a precision of 6%. The detection and quantification limits for ochratoxin A were 0.2 and 0.8 ng g−1 for the developed method, respectively, which is lower than the European Union regulatory limit of toxicity for ochratoxin-A (5 ng g−1) in coffee. Furthermore, the newly developed modified IS-FaMEx-ESI-MS/MS exhibited lower signal suppression of 8% with a good green metric score of 0.64. In addition, the IS-FaMEx-ESI-MS/MS showed good extraction recovery, matrix elimination, good detection, and quantification limits with high accuracy and precision due to the fewer extraction steps with semi-automation. Therefore, the presented method can be applied as a potential methodology for the detection of mycotoxins in food products for food safety and quality control purposes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Ahmadi M, Elmongy H, Madrakian T, Abdel-Rehim M (2017) Nanomaterials as sorbents for sample preparation in bioanalysis: a review. Anal Chim Acta 958:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.11.062
Cina M, del Ponce MV, Martinez LD, Cerutti S (2021) Development of a novel UHPLC-MS/MS method for the determination of ochratoxin A in tea. Heliyon 7:e06663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06663
Cina M, del Ponce MV, Fernandez L, Cerutti S (2022) A green approach for ochratoxin A determination in coffee infusions. J Food Compos Anal 114:104777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2022.104777
Commission Regulation (EC) 105/2010 of 5 February (2010) Amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs as regards ochratoxin A. Off. J. Eur. Communities, L 35/8, 2010.
da Silva AS, Fonseca Alvarenga Pereira RG, de Azevedo LN et al (2020) Fungi associated to beans infested with coffee berry borer and the risk of ochratoxin A. Food Control 113:107204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107204
Doruk KH, Hecer C, Ulusoy B (2019) Et ve Et Ürünlerinde Mikotoksin Tehlikesi. Atatürk Üniversitesi Veteriner Bilimleri Dergisi 14:90–97. https://doi.org/10.17094/ataunivbd.449705
Erben J, Klicova M, Klapstova A et al (2022) New polyamide 6 nanofibrous sorbents produced via alternating current electrospinning for the on-line solid phase extraction of small molecules in chromatography systems. Microchem J 174:107084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.107084
Erkmen O, Bozoglu TF (2016) Foodborne intoxications. In: Erkmen O, Bozoglu TF (eds) Food microbiology principles into practice, vol 1. Microorganisms related to foods, foodborne diseases and food spoilage. Wiley, Oxford, Chicester, pp 186–207
Erkmen O, Bozoglu TF (2016b) Microbial food ingredients and enzyme applications in food processing. In: Erkmen O, Bozoglu TF (eds) Food microbiology principles into practice, vol 2. Microorganisms in food preservation and processing. Wiley, Chichester, pp 395–420
Farahbakhsh J, Delnavaz M, Vatanpour V (2017) Investigation of raw and oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes in fabrication of reverse osmosis polyamide membranes for improvement in desalination and antifouling properties. Desalination 410:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.01.031
Freire L, Braga PAC, Furtado MM et al (2020) From grape to wine: fate of ochratoxin A during red, rose, and white winemaking process and the presence of ochratoxin derivatives in the final products. Food Control 113:107167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107167
García-Moraleja A, Font G, Mañes J, Ferrer E (2015a) Development of a new method for the simultaneous determination of 21 mycotoxins in coffee beverages by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Food Res Int 72:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2015.02.030
García-Moraleja A, Font G, Mañes J, Ferrer E (2015b) Simultaneous determination of mycotoxin in commercial coffee. Food Control 57:282–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.04.031
Gill R, Nadeem Q, Bououdina M (2016) Adsorption and desorption on nanostructured materials. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 112–138
Gros M, Rodríguez-Mozaz S, Barceló D (2013) Rapid analysis of multiclass antibiotic residues and some of their metabolites in hospital, urban wastewater and river water by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole-linear ion trap tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1292:173–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2012.12.072
Gurrani S, Prakasham K, Pasupuleti RR et al (2022) Rapid in-syringe-based ultrasonic-energy assisted salt-enhanced homogeneous liquid-liquid microextraction technique coupled with HPLC/low-temperature evaporative light-scattering detector for quantification of sodium hyaluronate in food products. Microchem J 172:106898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106898
Herrera López S, Scholten J, Kiedrowska B, de Kok A (2019) Method validation and application of a selective multiresidue analysis of highly polar pesticides in food matrices using hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1594:93–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.02.024
Iqbal SZ, Mumtaz A, Mahmood Z et al (2021) Assessment of aflatoxins and ochratoxin a in chili sauce samples and estimation of dietary intake. Food Control 121:107621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107621
Kaewsuya P, Brewer WE, Wong J, Morgan SL (2013) Automated QuEChERS tips for analysis of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables by GC-MS. J Agric Food Chem 61:2299–2314. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf304648h
Keçili R, Büyüktiryaki S, Hussain CM (2019) Advancement in bioanalytical science through nanotechnology: past, present and future. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 110:259–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.11.012
Malir F, Ostry V, Pfohl-Leszkowicz A, Roubal T (2012) Ochratoxin A exposure biomarkers in the czech republic and comparison with foreign countries. Biomarkers 17:577–589. https://doi.org/10.3109/1354750X.2012.692392
Malir F, Ostry V, Pfohl-Leszkowicz A et al (2014) Transfer of ochratoxin A into tea and coffee beverages. Toxins (basel) 6:3438–3453. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6123438
Moretti A, Logrieco AF, Susca A (2017) Mycotoxins: an underhand food problem. Springer, New York, pp 3–12
Pasupuleti RR, Tsai P-C, Ponnusamy VK (2021) Low-cost disposable poly(ethyleneimine)-functionalized carbon nanofibers coated cellulose paper as efficient solid phase extraction sorbent material for the extraction of parahydroxybenzoates from environmental waters. Chemosphere 267:129274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129274
Pena-Pereira F, Wojnowski W, Tobiszewski M (2020) AGREE—analytical GREEnness metric approach and software. Anal Chem 92(14):10076–10082
Ren X, Balavandy SK, Li F et al (2022) Miniaturized 3D printed solid-phase extraction cartridges with integrated porous frits. Anal Chim Acta 1208:339790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2022.339790
Sakin F, Tekeli İO, Yipel M, Kürekci C (2018) Occurrence and health risk assessment of aflatoxins and ochratoxin a in Sürk, a Turkish dairy food, as studied by HPLC. Food Control 90:317–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.03.012
Seebunrueng K, Santaladchaiyakit Y, Srijaranai S (2014) Vortex-assisted low density solvent based demulsified dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides in water samples. Chemosphere 103:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.11.024
Seebunrueng K, Santaladchaiyakit Y, Srijaranai S (2015) Vortex-assisted low density solvent liquid–liquid microextraction and salt-induced demulsification coupled to high performance liquid chromatography for the determination of five organophosphorus pesticide residues in fruits. Talanta 132:769–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.10.020
Song L, Zeng W, Li A et al (2022) Automated multi-plug filtration cleanup method for analysis of 48 pesticide residues in green tea using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Control 131:108436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108436
Vargas EA, dos Santos EA, Pittet A et al (2005) Determination of ochratoxin A in green coffee by immunoaffinity column cleanup and liquid chomatography: collaborative study. J AOAC Int 88:773–779. https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoac/88.3.773
Yan Y, Deng C (2019) Recent advances in nanomaterials for sample pre-treatment in phosphoproteomics research. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 120:115655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.115655
Zhang Y, Li G, Wu D et al (2019) Recent advances in emerging nanomaterials based food sample pretreatment methods for food safety screening. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 121:115669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.115669
Zhang X, Zhang L, Zhou T, Zhou Y (2022) Fungal flora and mycotoxin contamination in tea: current status, detection methods and dietary risk assessment—A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci Technol 127:207–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2022.05.019
Acknowledgements
Authors like to thank Kaohsiung Medical University for providing the vital resources for this research.
Funding
This work was supported partially by the Research Center for Precision Environmental Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan from The Featured Areas Research Center Program within the framework of the Higher Education Sprout Project by the Ministry of Education (MOE) in Taiwan and by Kaohsiung Medical University Research Center Grant (KMUTC112A01). This work was also supported financially by the grant MOST-110-2113-M-037-009- from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan. This research work was also supported financially by the bilateral grant from 109KN007 (KMU-NSYSU), Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KP, SG: Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Validation, Writing-Original Draft; JS, MTU, RRS, AKP: Conceptualization, Resources, Investigation, Validation; CDD, YCL, BT, PCH, GA: Data Curation, Visualization; Supervision; VKP: Methodology, Resources, Writing—Review & Editing, Supervision, and Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Confict of interest
The authors declare no confict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All authors have seen and approved the submitted version of the manuscript to JFST.
Consent for publication
All authors consented for publishing the work. All authors agree to publish an individual’s data or image in JFST.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Prakasham, K., Gurrani, S., Shiea, J. et al. Facile analysis of mycotoxin in coffee and tea samples using a novel semi-automated in-syringe based fast mycotoxin extraction (FaMEx) technique coupled with direct-injection ESI-MS/MS analysis. J Food Sci Technol 60, 1992–2000 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05733-z
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05733-z